Yield Farming Explained: A Beginner’s Guide to Earning Passive Income in Crypto
Cryptocurrency is no longer just about trading Bitcoin or Ethereum. Over the last few years, decentralized finance (DeFi) has emerged as a powerful trend in the crypto space, offering new ways for investors to earn passive income. One of the most popular methods in the DeFi ecosystem is yield farming. This blog post will explain the following:
- how yield farming works,
- how it can generate passive income,
- and the risks and rewards involved.
1 - What is Yield Farming?
Yield farming is the process of earning rewards, typically in the form of cryptocurrency, by lending or staking your digital assets in decentralized finance protocols. Essentially, it involves providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or lending protocols in exchange for interest or additional tokens. Yield farming is powered by smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code—on blockchain networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Polygon.
Think of it as putting your money to work. Instead of letting your crypto sit idle in a wallet, you can lend it out to others, provide liquidity for trading pairs, or stake it in a protocol and receive returns in exchange. The rewards you earn often come in the form of the platform’s native token or other cryptocurrencies, depending on the protocol.

2 - How Does Yield Farming Work?
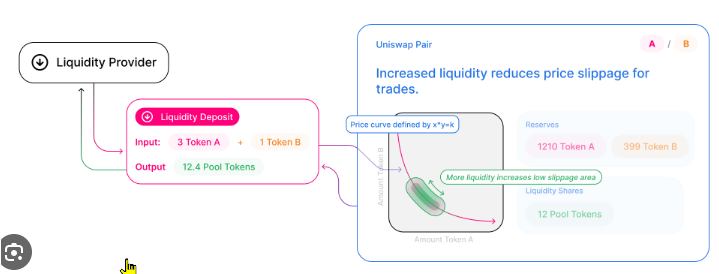
Yield farming operates through liquidity pools, which are pools of tokens locked in a smart contract that facilitate decentralized trading, lending, or borrowing. Users, called liquidity providers (LPs), deposit their crypto assets into these pools. In return, they receive tokens representing their share of the pool, and they earn a portion of the transaction fees generated by the pool or other forms of rewards.
Here’s how yield farming works in a step-by-step breakdown:
Liquidity Providers Deposit Funds: LPs deposit their tokens, such as Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT), or DAI, into a liquidity pool. These funds are used by decentralized applications (dApps) to provide liquidity for various DeFi activities, such as lending, borrowing, or token swapping.
Smart Contracts Manage the Pool: A smart contract manages the liquidity pool, ensuring that the rules of the protocol are followed without the need for intermediaries like banks or brokers.
Rewards Accumulation: LPs earn rewards, typically in the form of additional tokens, for providing liquidity. The rewards can be from transaction fees, interest on loans, or incentives provided by the platform itself (such as governance tokens).
Withdrawal of Funds: LPs can withdraw their funds from the pool, along with the rewards they have accumulated, at any time unless there is a lock-up period.
3 - Common Yield Farming Strategies
There are different strategies for yield farming, each varying in complexity and risk. The following are some popular yield farming approaches:
Lending: One of the simplest and most common strategies is lending your crypto assets on platforms like Aave or Compound. Users lend their cryptocurrency in return for interest payments. These platforms use a pool of funds from lenders to issue loans to borrowers. The lenders receive interest for providing liquidity.
Staking: Staking involves locking up your tokens in a network to help secure the blockchain and validate transactions. In return, you receive staking rewards. Some DeFi platforms offer additional incentives for staking their governance tokens, which can boost your returns.
Liquidity Provision: By providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges like Uniswap or SushiSwap, you can earn a share of the transaction fees generated by the exchange. However, providing liquidity exposes you to impermanent loss, which occurs when the value of your deposited tokens fluctuates significantly compared to when you initially deposited them.
Yield Aggregators: Yield aggregators like Yearn Finance and Autofarm are platforms that automatically move your funds between different DeFi protocols to optimize returns. They combine various farming strategies to maximize the yield for their users, helping investors earn more by finding the best opportunities across multiple platforms.
Dual-Asset Farming: In dual-asset farming, you deposit a pair of cryptocurrencies into a liquidity pool. For example, on Uniswap, you might deposit ETH and DAI into a pool that facilitates trading between these two tokens. In return, you earn a portion of the fees generated by traders who use the pool.
4 - Key Metrics in Yield Farming
When deciding where to farm, it’s important to understand the key metrics that determine your potential returns:
Annual Percentage Yield (APY): This is a key measure in yield farming and represents the projected return on an investment over the course of a year. APY accounts for compounding, meaning the interest earned on the initial investment is reinvested and earns interest as well. Higher APYs often come with higher risks.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR): Unlike APY, APR does not account for compounding. It’s a simpler calculation that measures the yearly interest rate without reinvesting earned interest. Yield farmers often compare APR and APY when choosing where to deposit funds.
Total Value Locked (TVL): This metric refers to the total amount of assets locked into a DeFi protocol. TVL is a good indicator of the protocol’s popularity and liquidity. A higher TVL generally signifies more confidence from users and a larger pool of liquidity.
Liquidity Mining: In liquidity mining, DeFi platforms reward users with tokens for providing liquidity. These tokens can either be sold for profit or staked for further rewards, and they often serve as governance tokens that give holders voting rights in the platform’s development.
5 - Benefits of Yield Farming
Yield farming has become popular because it offers several compelling benefits:
High Potential Returns: Compared to traditional savings accounts or even stock market investments, yield farming can offer extremely high returns. APYs in DeFi can range from 5% to over 100%, depending on the risk and the protocol.
Decentralization: Yield farming operates without intermediaries, meaning you can earn passive income without going through banks, brokers, or other traditional financial institutions.
Compound Interest: In many protocols, the rewards earned can be reinvested into the pool, allowing you to benefit from the power of compound interest. This means that the rewards you earn start earning additional rewards.
Liquidity Provider Incentives: Many DeFi platforms offer additional incentives to LPs in the form of native tokens or governance tokens, which can boost returns even further.
6 - Risks of Yield Farming
While the potential returns in yield farming are attractive, it’s important to be aware of the risks involved:
Impermanent Loss: This occurs when the value of your deposited assets changes compared to when you first deposited them in the liquidity pool. If the price of one token in the pair increases significantly, your share of the pool may become worth less than simply holding the tokens outside the pool.
Smart Contract Risks: Yield farming is powered by smart contracts, which are not infallible. Bugs in the code or vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers, leading to the loss of funds.
Volatility: Many yield farming platforms rely on volatile cryptocurrencies, and the value of these assets can fluctuate drastically. This adds another layer of risk for investors who may see their holdings depreciate quickly in a downturn.
Rug Pulls and Scams: A rug pull occurs when the developers of a DeFi project abandon the platform and take the funds with them. It’s crucial to research the credibility of a platform before depositing assets.
7 - How to Get Started with Yield Farming
If you’re ready to explore yield farming, follow these steps to get started:
Choose a Platform: Decide which DeFi platform to use. Popular platforms for yield farming include Aave, Compound, Uniswap, SushiSwap, and Yearn Finance. Consider factors like APY, TVL, and the platform’s reputation. Click Here for Your Free Blueprint to setup your Crypto Yield Farm and earn Daily Passive Income.
Create a Wallet: You’ll need a crypto wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet to connect to DeFi platforms. These wallets allow you to manage your tokens and interact with decentralized applications.
Deposit Assets: Once your wallet is set up and funded with crypto, you can deposit your assets into a DeFi protocol’s liquidity pool or lending platform.
Monitor and Reinvest: Yield farming requires active monitoring, especially if you’re dealing with volatile assets. You can reinvest your rewards to compound your returns or withdraw them as needed.

Conclusion
Yield farming has opened up new ways for crypto investors to earn passive income by putting their assets to work in DeFi protocols. With potentially high returns, it’s an attractive alternative to traditional banking products, but it also comes with significant risks. Before diving in, it’s essential to do thorough research, understand the risks, and start small until you become more comfortable with how yield farming works.
As the DeFi space continues to evolve, yield farming will likely remain a central strategy for earning passive income in the crypto world. For those willing to take on the risks, it offers an exciting opportunity to participate in the growing decentralized finance ecosystem and benefit from its innovative potential.
