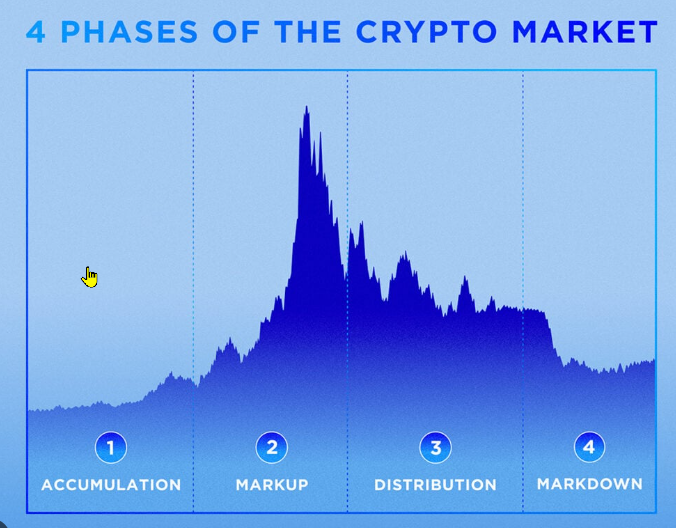
The Four Phases of the Cryptocurrency Market Cycle: How to Identify and Profit from Each Phase
Introduction
The cryptocurrency market, like traditional financial markets, moves in cycles. These cycles are often intense, with dramatic shifts in sentiment and price that can be both exhilarating and intimidating. Understanding these cycles is essential for investors looking to navigate the crypto market effectively and make well-timed decisions that can lead to significant gains.
In this post, we’ll break down the four main phases of the cryptocurrency market cycle, discussing how to recognize each phase, the factors driving these cycles, and strategies you can employ to maximize profits in every stage. Whether you’re new to crypto or a seasoned investor, understanding the cyclical nature of the market can help you stay ahead of trends and avoid costly mistakes.
What Are Market Cycles?
Market cycles refer to recurring patterns in the movement of asset prices and investor sentiment. In crypto, these cycles are often shorter and more volatile than in traditional markets, given the high level of speculation, relatively low market liquidity, and constant influx of new technologies.
The cryptocurrency market generally follows four main phases:
- Accumulation Phase
- Markup Phase
- Distribution Phase
- Markdown Phase
These phases repeat in a cycle and are often driven by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory news, economic conditions, and shifts in investor sentiment. Let’s explore each phase in detail.
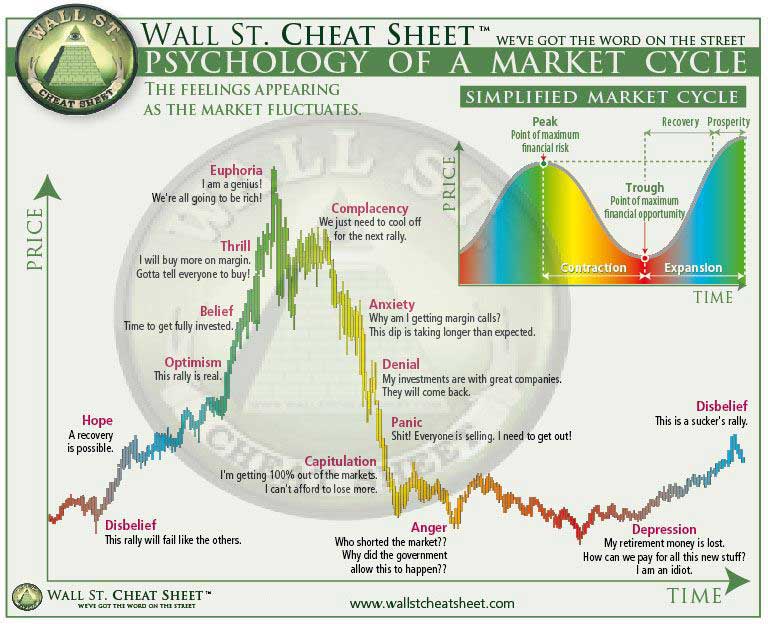
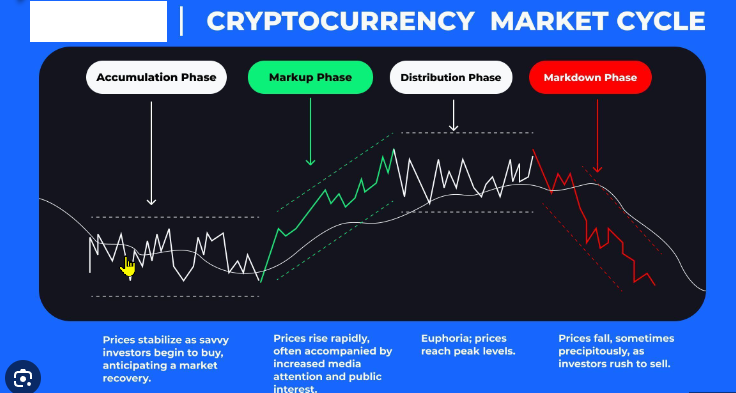
Phase 1: The Accumulation Phase
Overview:
The accumulation phase is the period after a significant price decline, often following the end of a bear market. During this phase, sentiment is generally low as investors have experienced significant losses and may be wary of further investments. Prices tend to stabilize and remain relatively flat as selling pressure decreases and buying interest starts to increase gradually.
Characteristics:
- Low trading volume
- Stable or slightly rising prices
- Bearish sentiment gradually turning neutral
- Experienced investors and “smart money” starting to buy in
Investor Strategy:
For seasoned investors, the accumulation phase is a buying opportunity. Since prices are lower and tend to stay stable, this phase offers a good entry point for those who have done their research and believe in the long-term potential of specific cryptocurrencies. Look for projects with strong fundamentals that can withstand the test of time and avoid “hype” coins that may not survive the next cycle.
How to Profit:
The accumulation phase is ideal for building long-term positions. For those who are new to crypto, this is the time to accumulate assets cautiously. Setting up a dollar-cost averaging (DCA) strategy, where you invest a fixed amount at regular intervals, can help mitigate risks and gradually build a position.
Phase 2: The Markup Phase
Overview:
The markup phase is where the excitement begins. After a prolonged period of price stability, prices start to rise as investor sentiment improves. This is often sparked by positive news, increased mainstream adoption, or signs of economic recovery. As prices climb, more investors take notice, and “fear of missing out” (FOMO) drives up demand, pushing prices higher.
Characteristics:
- Rising trading volumes
- Increasing prices, often at a rapid pace
- Media attention grows, drawing new investors
- Positive sentiment and early signs of euphoria
Investor Strategy:
During the markup phase, early investors can see substantial returns as prices begin to surge. However, it’s crucial to remain cautious as FOMO can lead to impulsive buying. Assess the fundamentals of the assets you hold and avoid investing heavily in projects solely based on hype. At this stage, setting up a profit-taking strategy, such as selling a small percentage of your holdings at certain price targets, can lock in gains while still allowing you to benefit from future upside.
How to Profit:
For experienced traders, the markup phase is ideal for short-term trading and swing trading, where you capitalize on upward momentum. Technical analysis tools such as moving averages, support and resistance levels, and RSI (Relative Strength Index) can be helpful in identifying optimal entry and exit points. Remember that while the markup phase offers excellent profit potential, risks are high as volatility increases.
Phase 3: The Distribution Phase
Overview:
The distribution phase occurs when prices have reached a peak, and the upward momentum begins to slow. Investor sentiment shifts from euphoria to caution as early investors start taking profits. During this phase, the price may fluctuate within a tight range, as buyers and sellers reach a point of equilibrium.
Characteristics:
- High trading volumes as both buying and selling intensify
- Prices move sideways within a range, creating a “top”
- Increasingly mixed sentiment, with signs of uncertainty
- Smart money and early investors gradually offloading holdings
Investor Strategy:
The distribution phase is a signal for cautious investors to consider selling some or all of their holdings. Since prices are near peak levels, this is an ideal time to lock in profits. Resist the temptation to hold onto assets in hopes of even higher prices, as this phase often precedes a downward trend.
How to Profit:
Implementing a stop-loss strategy at this stage can protect your gains in case of a sharp downturn. Consider gradually selling portions of your holdings as prices hit certain targets, known as scaling out. For those looking to short-sell, the distribution phase can also be a prime opportunity to capitalize on a potential downturn.
Phase 4: The Markdown Phase
Overview:
The markdown phase marks the beginning of a bear market. Prices start to decline as selling pressure mounts, and bullish sentiment fades. The markdown phase can be swift or prolonged, depending on the reasons behind the decline, such as regulatory news, economic downturns, or loss of investor interest. This phase can result in panic selling as prices fall, often leading to significant losses for those who bought during the later stages of the markup phase.
Characteristics:
- Sharp decline in prices and trading volumes
- Fearful sentiment, with pessimism and panic selling
- Media attention shifts from positive to negative
- General market disinterest and investor caution
Investor Strategy:
During the markdown phase, it’s wise to exercise patience. Attempting to “catch the bottom” can be risky, as prices may continue to fall. For long-term investors, this phase can offer buying opportunities, but only for projects with strong fundamentals. Wait for signs of stabilization before making significant investments, as further declines can erode your capital.
How to Profit:
Traders with experience in short selling can capitalize on the markdown phase by betting on price declines. Inverse ETFs, options trading, or short positions on crypto futures can be used to profit in a downtrend. Alternatively, holding stablecoins or converting assets to fiat currency can preserve capital during the markdown phase. This capital can later be used to re-enter the market at a lower price point once signs of accumulation appear.
Factors Influencing Crypto Market Cycles
Crypto cycles are heavily influenced by external factors, including:
- Macroeconomic Conditions: Interest rates, inflation, and global economic stability play a role in the behavior of financial markets, including crypto.
- Regulatory Developments: News of crypto regulations can dramatically impact investor sentiment, often triggering large sell-offs or buy-ins.
- Technology and Adoption: Breakthroughs in blockchain technology, such as major upgrades to networks like Ethereum, can drive new interest and adoption.
- Market Sentiment and Media Influence: Social media, news platforms, and public figures can influence cycles, especially with the high degree of speculation in the crypto space.
Mastering the Crypto Cycle: Tips for Success
- Stay Informed: Follow market news, regulatory updates, and technological advancements to anticipate shifts in the cycle.
- Practice Risk Management: Implement stop-losses, diversify your holdings, and don’t invest more than you can afford to lose.
- Use Technical Analysis: Study price charts and use technical indicators to identify potential market reversals and trends.
- Adopt a Long-Term Mindset: While the crypto market is volatile, those who focus on quality projects and hold through cycles often see significant returns over time.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the four phases of the cryptocurrency market cycle—accumulation, markup, distribution, and markdown—can give you an edge as an investor. Each phase presents unique opportunities and risks, and by recognizing the signs of each stage, you can tailor your strategy accordingly. Remember, while the potential for profit is high, so are the risks, making it essential to combine a disciplined approach with a solid understanding of market dynamics.
Mastering the crypto market cycle doesn’t guarantee profits, but it can help you make better decisions, avoid costly mistakes, and increase your chances of success in the ever-changing world of cryptocurrency.