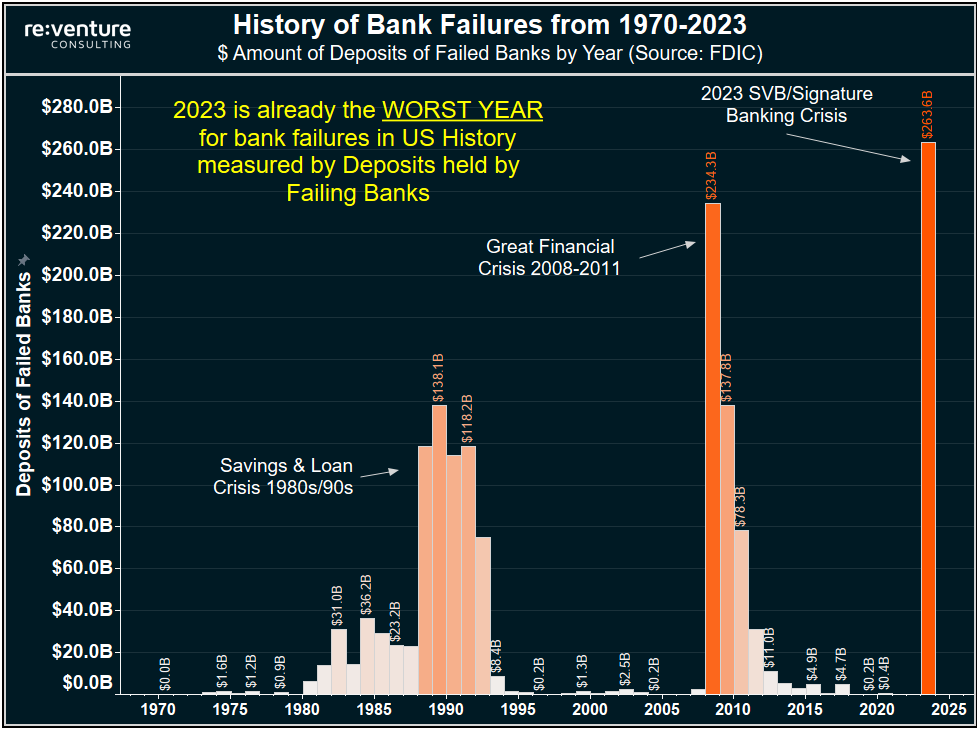
Which Banks Failed in 2008? Could this happen again?
During the global financial crisis of 2008, a significant number of banks and financial institutions failed or were in danger of failing. While I can’t provide an exact number, I can give you an overview of some of the notable bank failures and the reasons behind them:

Lehman Brothers: Perhaps the most famous bank failure during the 2008 financial crisis, Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy in September 2008. It was heavily involved in risky mortgage-backed securities and suffered massive losses when the housing market collapsed.
Washington Mutual (WaMu): Washington Mutual, a large savings and loan association, was seized by the U.S. government and placed into receivership in September 2008. Its failure was largely due to its high exposure to subprime mortgages.
Bear Stearns: In March 2008, Bear Stearns was sold to JPMorgan Chase in a government-backed deal to prevent its collapse. It faced a liquidity crisis because of its heavy involvement in mortgage-backed securities.
IndyMac Bank: IndyMac Bank was seized by regulators in July 2008 due to its significant exposure to risky mortgages, and it became one of the largest bank failures in U.S. history.
Wachovia: Wachovia Corporation suffered heavy losses from its exposure to subprime mortgages and was acquired by Wells Fargo in a government-assisted transaction in October 2008.
AIG: While not a traditional bank, American International Group (AIG) faced a severe financial crisis due to its involvement in insuring mortgage-backed securities. The U.S. government provided a massive bailout to prevent its collapse.
Conclusion
These are just a few examples of the bank failures and financial crises that occurred in 2008. The financial crisis had its roots in the housing market bubble, subprime mortgage lending, and the subsequent collapse of housing prices. Many banks and financial institutions had invested heavily in mortgage-backed securities and derivatives linked to these securities, which became worthless when the housing market collapsed. This led to widespread losses, liquidity problems, and ultimately the failure or near-failure of several major financial institutions.